|
|
Nutrient Management :: Methods of Fertilizers Application |
|
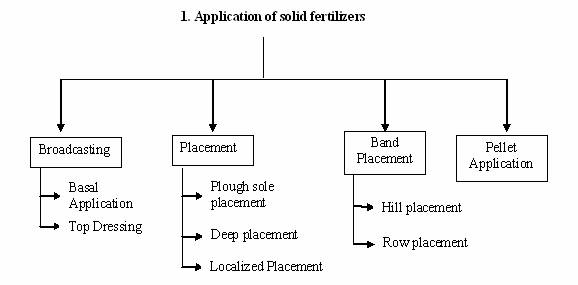
METHODS OF FERTILIZER APPLICATION The different methods of fertilizer application are as follows:
a) Broadcasting
Broadcasting of fertilizers is of two types. i) Broadcasting at sowing or planting (Basal application) The main objectives of broadcasting the fertilizers at sowing time are to uniformly distribute the fertilizer over the entire field and to mix it with soil. ii) Top dressing It is the broadcasting of fertilizers particularly nitrogenous fertilizers in closely sown crops like paddy and wheat, with the objective of supplying nitrogen in readily available form to growing plants. Disadvantages of broadcasting The main disadvantages of application of fertilizers through broadcasting are: b) Placement
The most common methods of placement are as follows: i) Plough sole placement
ii) Deep placement It is the placement of ammoniacal nitrogenous fertilizers in the reduction zone of soil particularly in paddy fields, where ammoniacal nitrogen remains available to the crop. This method ensures better distribution of fertilizer in the root zone soil and prevents loss of nutrients by run-off. iii) Localized placement It refers to the application of fertilizers into the soil close to the seed or plant in order to supply the nutrients in adequate amounts to the roots of growing plants. The common methods to place fertilizers close to the seed or plant are as follows: a) Drilling In this method, the fertilizer is applied at the time of sowing by means of a seed-cum-fertilizer drill. This places fertilizer and the seed in the same row but at different depths. Although this method has been found suitable for the application of phosphatic and potassic fertilizers in cereal crops, but sometimes germination of seeds and young plants may get damaged due to higher concentration of soluble salts. b) Side dressing It refers to the spread of fertilizer in between the rows and around the plants. The common methods of side-dressing are
c) Band placement If refers to the placement of fertilizer in bands. Band placement is of two types. i) Hill placement It is practiced for the application of fertilizers in orchards. In this method, fertilizers are placed close to the plant in bands on one or both sides of the plant. The length and depth of the band varies with the nature of the crop. ii) Row placement When the crops like sugarcane, potato, maize, cereals etc., are sown close together in rows, the fertilizer is applied in continuous bands on one or both sides of the row, which is known as row placement.
d) Pellet application
Advantages of placement of fertilizers The main advantages are as follows:
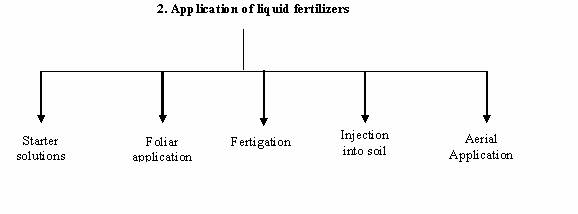
Following are the common methods of applying liquid fertilizers a) Starter solutions It refers to the application of solution of N, P2O5 and K2O in the ratio of 1:2:1 and 1:1:2 to young plants at the time of transplanting, particularly for vegetables. b) Foliar application
c) Application through irrigation water (Fertigation)
d) Injection into soil
e) Aerial application. In areas where ground application is not practicable, the fertilizer solutions are applied by aircraft particularly in hilly areas, in forest lands, in grass lands or in sugarcane fields etc. |
|
| Home | Seasons & Varieties | Tillage | Nutrient Management | Irrigation Management | Weed Management | Crop Protection | Cost of Cultivation | © All Rights Reserved. TNAU-2014. |
|