Saline Soil
A soil containing excess of natural soluble salts to impair soil and crop productivity and has pH value of 8.5, EC 4 mmhos per cm at 25 degree C and ESP 15 per cent.
Scion
A bud or branch cut for grafting or planting.
Section
A surveyed parcel of land containing 640 acres one square mile.
Seedstock
Pedigreed or well-bred livestock which is maintained for breeding purposes. A specially selected strain of plants or seeds which are to be used as parents for future generations.
Silage
A crop that has been preserved in a moist, succulent condition by partial fermentation in a tight container (silo) above or below ground. The chief crops stored in this way are corn (the whole plant), sorghum, and various legumes and grasses. The main use of silage is in cattle feed.
Sire
The male parent.
Sorghum
A cereal grass used mainly for feedgrain or silage.
Sow
A sexually mature female hog, after having her first litter.
Soybeans
A legume crop, native to the Orient, used mainly in the United States for high protein feed and oil.
Specific Humidity
Specific Humidity is the weight of water vapour per unit weight of air
(including water vapour)
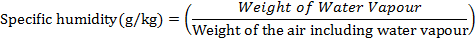
Stag
A male bovine castrated after puberty.
Stallion
An unaltered (uncastrated) male horse.
Stand
A recognizable area of plants that is relatively homogeneous and can be managed as a single unit.
Steer
A male bovine castrated early in life, usually as a calf.
Stockers (or stocker cattle)
Heifers and/or steers that are being grown on pasture or other forage for later sale as feedlot replacements.
Secondary tillage
The tillage operations following primary tillage to create a good seed bed for proper seeding/planting.
Selective herbicide
It is that which is more toxic to one plant, some may be killed and others may be affected only slightly or not at all.
Sequence cropping
In this system, harvesting of the first crop is followed by the planting of the second crop, after fresh land preparation. Sequence cropping is adopted when water resources are adequately available till the maturing of the crop that is grown after the first crop. Sequence crops that are ideal after rice are mustard, pulses, maize, tomato, groundnut and vegetables.
Shelter belt
It is a belt of trees and shrubs intended to protect field crop from wind and to conserve soil moisture. A good shelterbelt reduces wind velocity on the windward side from 5 to 10 times the height of the trees and on the leeward side from 10-30 times its height. Trees about 50 feet in height would protect an area approximately 400 m in width. The shelterbelt should consist of several rows of trees and trees of varying heights. A high row of shrubs on the windward side can provide a dense barrier to the wind. This arrangement ensures that the foliage of the shelterbelt lifts the wind well above ground level and gradually drops it downward on the other side of the shelterbelt. To have protection from the wind at all seasons both evergreen and deciduous trees are included in the shelterbelt.
Silage
Animal feed resulting from the storage and fermentation of green or wet crop under anaerobic conditions.
Silvihorticulture
Care and cultivation of small plots (gardens) devoted primarily to vegetables and fruits, including woody species.
Smothering
Those crops which are through their thick canopy exclude light and prevent all top growth of weeds.
Sodium adsorption ratio (SAR)
A ratio for soil extracts and irrigation waters used to express the relative activity of sodium ions in exchange reactions with soil.
Soil moisture tension
It is the force with which water held by soil against gravity. It is generally expressed in mm of mercury.
Sole cropping
Growing one crop variety in a pure stand.
Stratification
A method of breaking seed dormancy in which the imbibed seed are subjected to a period of chilling to after ripen the embryo.
Strip cropping
Growing soil conserving and soil depleting crops in alternate strips running perpendicular to the slope strips wide enough to permit independent cultivation but narrow enough for the crop to interact agronomically.
Stubble mulching
String the soil with implements that leaves considerable part of the vegetative material or crop residues or vegetable litter on the surface as a protection against erosion and for conserving moisture by favouring infiltration and reducing evaporation.
Substitution farming
It is farming enterprise, which provides food and commodities just sufficient for the farming family, and there is no surplus to sell.
Sustainable agriculture
Management of resources for agriculture to satisfy changing human needs, while maintaining or enhancing the quality of the environment and conserving the natural resources.
Systematic herbicide
A herbicide which is translocated within the plants.