BROILERS
Caring Broilers
Broilers are young chicken of either sex of six to eight weeks of age, tender meat with soft, pliable, smooth textured skin and flexible breast bone cartilage.
Housing
Provide 930 cm2 floor spaces per broiler chick. Provision must be made for adequate ventilation. The general management of broiler chicks is similar to those discussed under egg type chicks.
Feeding
Provide up to 2 weeks 5 cm and from 3 weeks to finish 10 cm linear feeder space per bird. Raise the level of the feeder as the birds grow. Do not fill the feeder more than half. If tube feeders are used, provide 3 nos. of 12 kg capacity feeders per 100 chicks.

Composition of broiler ration
| Ingredient |
Percentage inclusion |
| Starter (0-5 weeks) |
Finisher (6-7 weeks) |
| Yellow Maize |
47.00 |
54.50 |
| Rice polish |
8.00 |
10.00 |
| Soyabean meal |
17.50 |
14.00 |
| Groundnut cake (expeller) |
15.00 |
11.00 |
| Unsalted dried fish |
10.00 |
8.00 |
| Mineral mixture |
2.00 |
2.00 |
| Salt |
0.50 |
0.50 |
| |
100.00 |
100.00 |
Alternatively commercial broiler starter and finisher rations prepared by reputed feed manufacturers can be given.
(Source: www.vuatkerala.org )
Watering
- 3 weeks to finish - 2 x 5 litres capacity waterers.
- Ensure clean fresh water always.
- Exercise extreme care and attention during the brooding period. If the losses in the first few days exceed 2%, carefully check the brooding management and get the postmortem examination done.
- Reduce brooder temperature every week by 3oC. When the brooder is removed provide one 40-watts bulb for every 250 broilers during night.
- To ascertain approximate quantity of feed and water that 100 broilers consume per day, the following formula given will be useful.
- Kg feed per 100 birds - Age in days/4.4
- Litres of water per 100 birds - Age in days/2.0
- The above formula will give approximate figures under average conditions. Depending on the season of the year, there is likely to be variations in the range of 5-10%.
Watering of Chicks
Vaccination programme for broiler chicken
| Age |
Disease |
Vaccine |
Route |
| 0-5 days |
RD |
Lasota or F vaccine |
Occulonasal |
| 10-14 days |
IBD |
IBD Live |
Drinking water |
| 24-28 days |
IBD |
|
Drinking water |
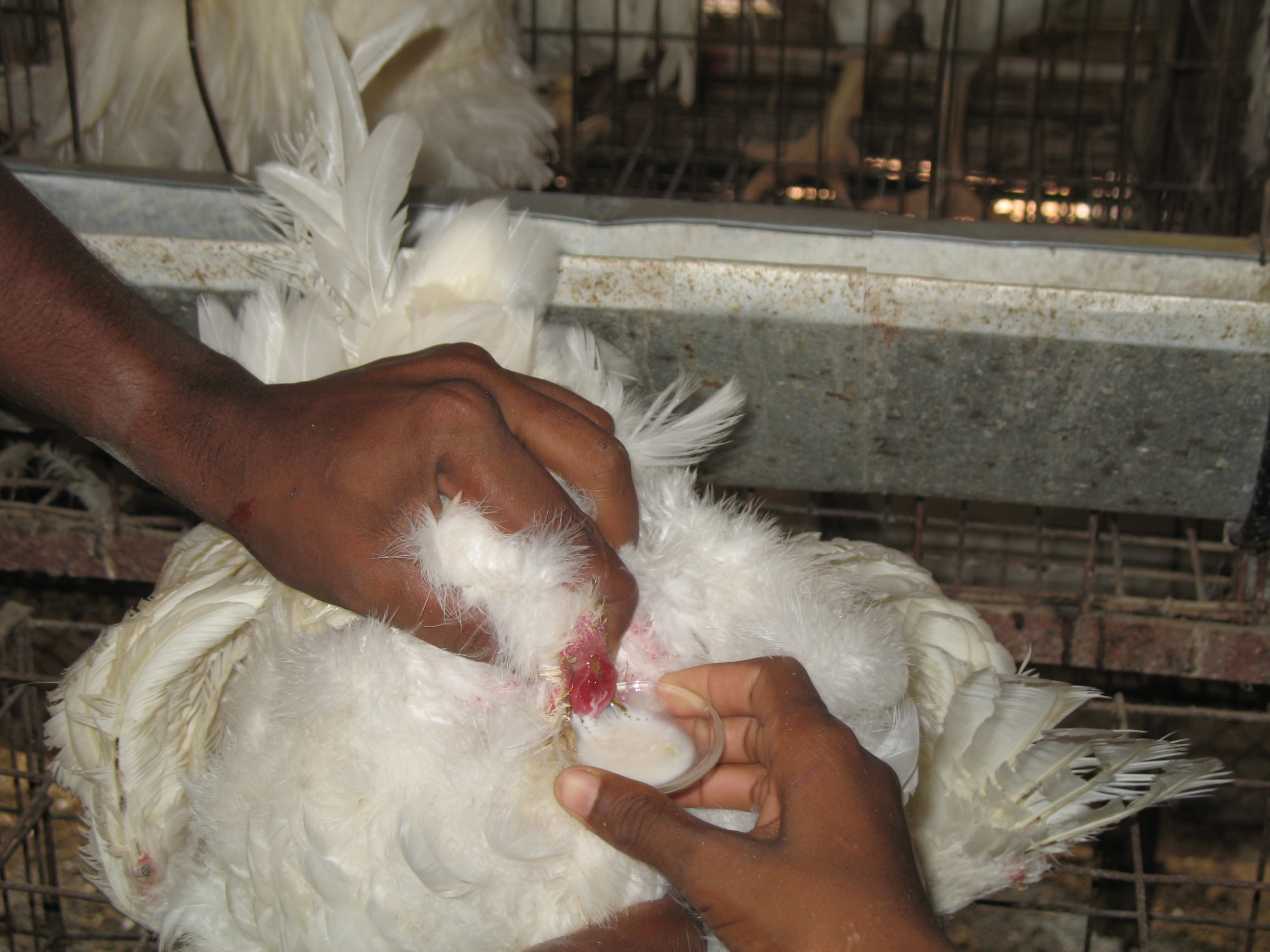  Vaccination
Vaccination
Production of Hatching Eggs
If hatching eggs are to be produced, cockerels have to be maintained. Rear at the rate of 15 cockerels per 100 pullets, cull- down to 12 cockerels at 10 weeks of age. For mating, provide one cock for 10-15 pullets of light breeds and 6-8 pullets of heavy breeds. Collect hatching eggs two weeks after introduction of males.
Gather hatching eggs 3 to 4 times a day. In hot or cold season increase the frequency of collections. As soon as the eggs are collected, store them at a temperature between 10 and 16oC with a relative humidity of 70 - 80%. Select eggs for hatching that meet the weight requirement and that are normal in shape, colour and texture. While storing and transporting hatching eggs, keep them with broad end up and handle the eggs very gently. If possible either set the eggs for incubation or market hatching eggs twice a week. Never hold hatching eggs for more than one week under ordinary conditions of storage.

Hatching conditions
The incubation period of chicken egg is 21 days. For successful hatching, eggs require specific conditions of temperature, turning and ventilation

Specific conditions for hatching
Temperature |
1-18 days
19-21 days |
37.5 – 37.8oC
36.9 –37.5oC |
| Humidity |
60% up to 18 days |
70% thereafter |
| Turning |
Once every 4 hours up to 18 days |
- |
| Ventilation |
1-18 days
19-21 days |
8 changes/hour
12 changes/hour |
(Source: Kerala Agricultural University)
Candling
Candle the eggs twice during incubation – one on 7th day and the other on 18-19 days of incubation. Transfer the eggs to the hatches after candling on 18th day.
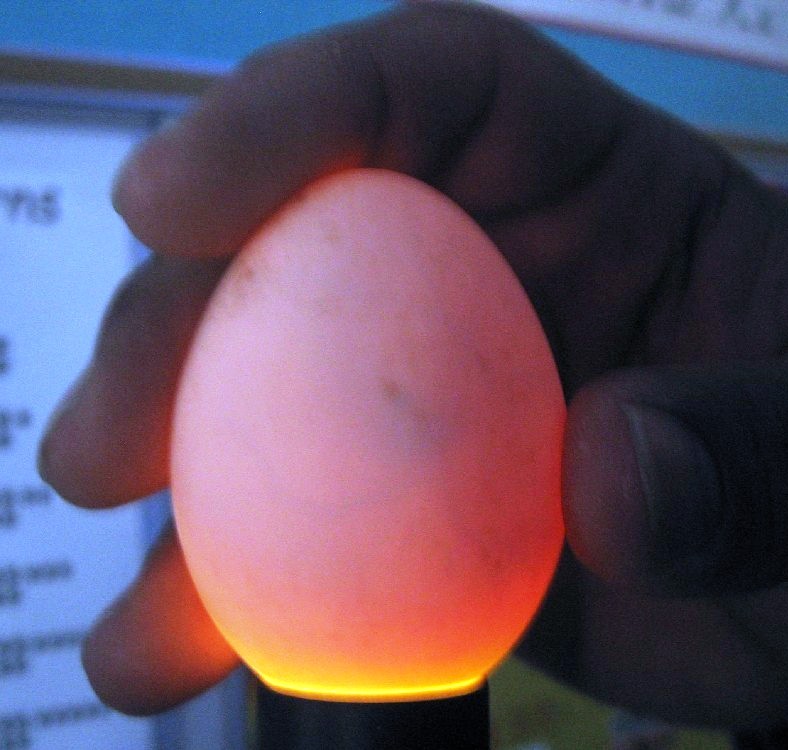

Candling
Disease Control Guidelines
Diseases are likely where larger numbers of birds are reared in confinement. Therefore, a planned programme for the prevention and control of diseases in the poultry houses is a crucial factor in profitable poultry farming. The following general principles are to be followed.
- Clean the house at least two weeks before housing a new batch of birds.
- Remove all old litter and equipment. Clean the ceiling, walls and floor. Thorough sweeping and washing followed by treatment with disinfectants are necessary.
- Wash, disinfect and dry the equipment before placing in the house.
- Clean the light reflectors, replace burnt out bulbs and check electric connections.
- Keep all wild birds, rats, dogs and cats out of the farm.
- Do not allow visitors into the poultry houses.
- Burn or bury all dead birds immediately.
- Clean the waters and feeders daily with 1% ammonia solution.
- Change foot-bath at the entrance of poultry house daily.
- Adhere to strict sanitation in and around the poultry house.
- Remove wet litter immediately.
- Look for signs of ill health in the flock every time you enter the poultry house.
- Deworm the birds as and when required after peak production.
- If any disease is suspected, immediately obtain accurate diagnosis and follow recommendations of the poultry specialist consulted.
Mycotoxins in feed
Chicken show varying degrees of sensitivity to different mycotoxins. Presence of mycotoxins in feed is found to cause depressed growth in chickens, depressed egg production and egg weight in laying hens. It adversely affects fertility and hatchability also. Ducks are more sensitive to mycotoxins than chicken.
The feed ingredients and feed should be free from mycotoxins. Moisture content above 11% leads to mould growth. Spoilage during storage can be avoided by drying, keeping in air tight bins and reducing storage humidity. Screening of feed ingredients and compounded feed may be carried out regularly. Toxin binders and mould inhibitors may be added to feed for safety.
Disinfectants and their use
- Lysol: Used as a 1-2% solution. Effective general disinfectant, suitable for instrument; poultry equipments, foot-bath etc;
- Lime (CaOH powder): An inexpensive general disinfectant can be used as a white wash to walls. 2-5% solution will destroy most pathogenic organisms and their spores. Highly corrosive to skin.
- Bleaching powder: May be used as floor disinfectant in empty houses.
- Phenols (Cresol): Less toxic but costly. Usually used as a 2-4% solution for disinfecting poultry houses and equipments.
The general guide for vaccination for chicken
Name of Vaccine |
Route |
Age of birds |
| La Sota or F vaccine Ranikhet |
Intranasal drop |
3 to 7 days |
| Marek's vaccine (in Hatchery) |
Intramuscular |
1 day |
| Infectious Bronchitis (1st dose) |
Eye drops |
2 - 3 weeks |
| La Sota Ranikhet |
Drinking water |
5 - 6 weeks |
| Fowl Pox (1st dose) |
Wing Web |
7 - 8 weeks |
| R2B Ranikhet |
Sub cut or Intramuscular |
9 - 10 weeks |
| Infectious Bronchitis |
Eye drop or drinking water |
16 weeks |
| Fowl Pox (2nd dose) |
Skin Scarification |
18 weeks |
| La Sota (if necessary) Ranikhet |
Drinking Water |
20 weeks |
| La Sota (if necessary) Ranikhet |
Drinking Water |
40 weeks |
| IBD : |
| Mildly invasive vaccine |
Drinking Water |
0 - 3 day |
| Intermediately invasive vaccine |
Drinking Water |
15th day |
| Intermediately invasive vaccine |
Drinking Water |
28-30th day |
(Source: www.vuatkerala.org ) |