Integrated fish-pig farming in India
Fish-pig farming material flow
The raising of pigs can fruit-fully be combined with fish culture by constructing animal housing units on the pond embankment or over the pond in such a way that the wastes are directly drained into the pond. The system has obvious advantages:
- The pig dung acts as excellent pond fertilizer and raises the biological productivity of the pond and consequently increases fish production.
- Some of the fishes feed directly on the pig excrete which contains 70 percent digestible food for the fish.
- No supplementary feed is required for the fish culture, which normally accounts for 60 percent of the total input cost in conventional fish culture.
- The pond dikes provide space for erection of animal housing units.
- Pond water is used for cleaning the pigsties and for bathing the pigs.
- The system cannot be adopted in all parts of India due to religious consideration but it has special significance in certain areas as it can improve the socioeconomic status of weaker rural communities, especially the tribals who traditionally raise pigs and can take up fish-pig farming easily.
|
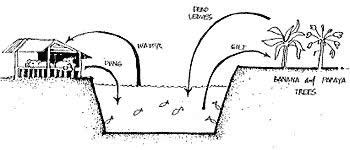
Fish-pig farming material flow |
| Culture practices
The ponds measuring about 1 000 m² may be located near your house, so that you can take care of the fish and pigs and can discourage poaching. Check and repair the dikes. The pond should be deep enough so as to retain more than 1 m water depth during the dry period.
Pond preparation
Drain and dry the pond to remove all the weeds and fish fauna remaining in the pond. If it is not possible to drain the pond, all the fish can be killed by applying 15 kg of both bleaching powder and urea for a 1 000 m² pond. Alternatively, 250 kg Mahua oil cake can be applied which kills all the fishes and also acts as organic pond fertilizer.
Pigs are brought to the pond before stocking the fish, so no basal application of manure is required. |
 |
Top |
Stocking
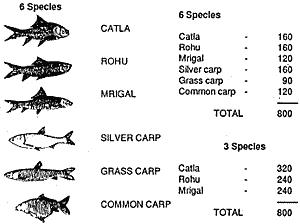
- Stock the pond with fingerlings 7 days after poisoning with bleaching powder. The recommended rate of stocking is:
- Alterations can be made on stocking density and species ratio, depending on the local conditions.
- Grass carp should be fed regularly with aquatic or terrestrial vegetation. Liming of the pond is done at regular intervals. It helps in stabilization of organic matter. About 25 kg lime shall be required for one year.
Harvesting
Due to abundance of natural food in the fish-pig pond, the fish attains marketable size within a few months. Partial harvesting, therefore, should be done three times, depending upon the growth of fish. Final harvesting may be done after 10-12 months. |
 |
Pig raising
The number of pigs required will depend upon the pond area. The excreta of three pigs are sufficient to fertilize a pond of 1 000 m². So three pigs may be raised on a pond of 0.1 ha. As pigs attain slaughter size within 5-6 months and fish raising of Indian exotic carp is done for 10-12 months, two lots of pigs can be raised along with one lot of fish.
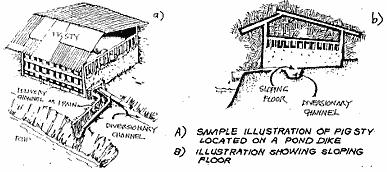
The pigsties are constructed on the pond embankments in such a way that the washings are drained to the pond through a delivery channel. A diversion channel is always provided to divert the excreta away from the ponds as these develop algal bloom or any other abnormality. Washings of pigsties are drained into the pond after sunrise to avoid oxygen depletion.
The pigsties can be constructed from any available cheap materials but the floor must be cemented with a slope towards the pond. Each pig is provided with a floor space of 1-1.5 m². |
 |

Integrated fish-pig farming |
|
Top |
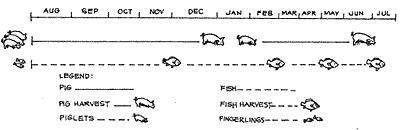
Calendar of activities for fish-pig farming
| Month |
Activities |
| August |
Pond Preparation, erection of pigsties, raising of piglets |
| September |
Stocking fingerlings, fattening and care of pigs |
| October |
Fattening and care of pigs and fish culture |
| November |
Fattening and care of pigs and fish culture |
| December |
First partial harvesting of fish |
| January |
Harvesting first lot of pigs |
| February |
Fattening of second lot of pigs |
| March |
Second partial harvesting of fish |
| April |
Fattening of pig and fish |
| May |
Third partial harvesting of fish |
| June |
Preparation for final harvesting of pigs and fish |
| July |
Final harvesting of fish and second lot of pigs |
Top
Source : http://www.fao.org/docrep/005/y1187e/y1187e16.htm
Updated on : May 2014 |

