Agricultural crops :: Pulses :: Blackgram
Root Rot and Leaf Blight: Rhizoctonia solani
| Field diagnostic symptoms |
-
Yellowing, drooping of leaves and death of plants
- Dark brown lesions on stem and bark shows shredding symptom.
- Easily pulled out leaving dried, rotten root portions in the ground
-
Black minute sclerotia on rotten stem and root tissues
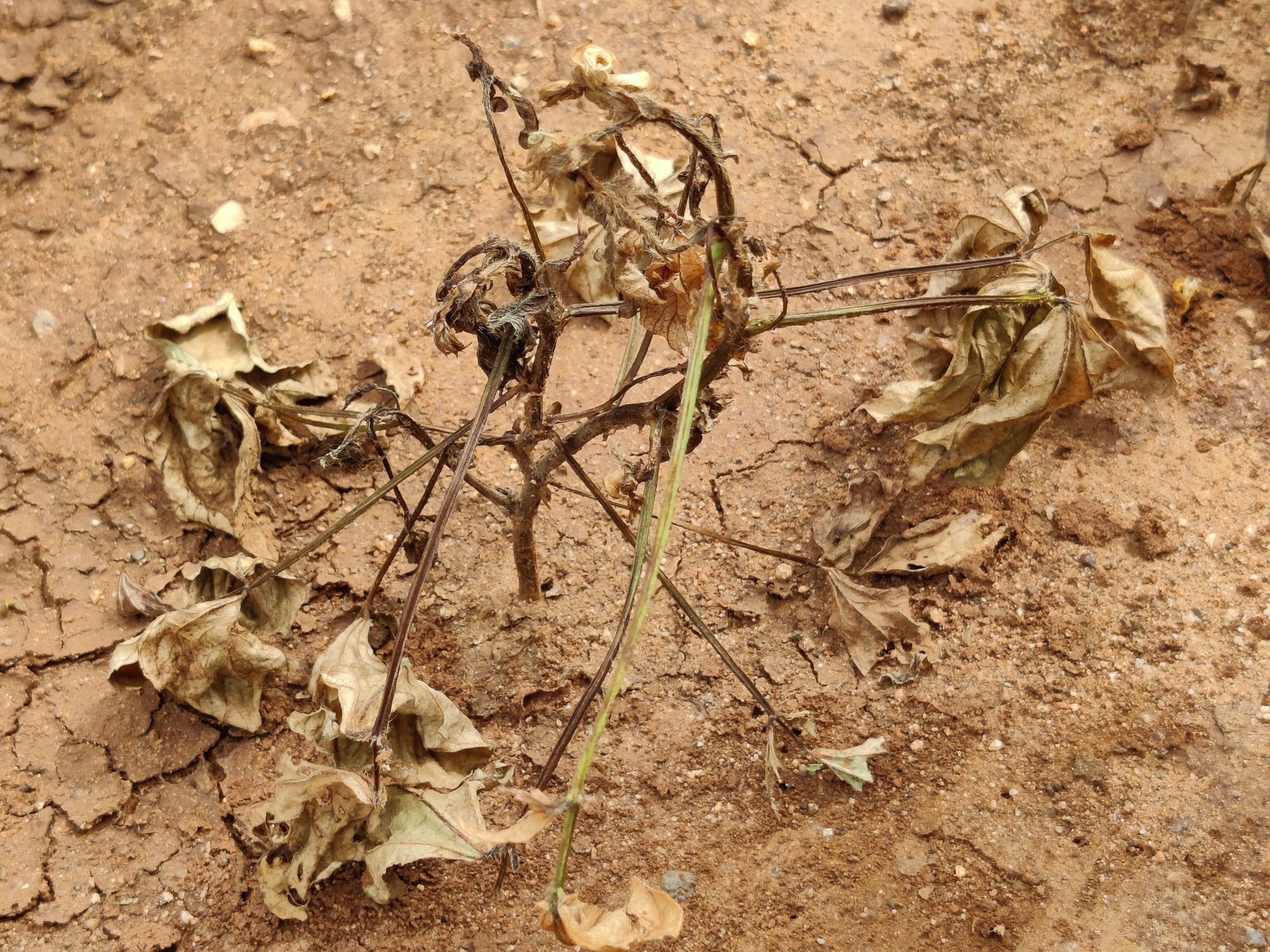 Dry root rot infected plant
Dry root rot infected plant
Causal agent
Rhizoctonia bataticola (Pycnidial stage: Macrophomina phaseolina)
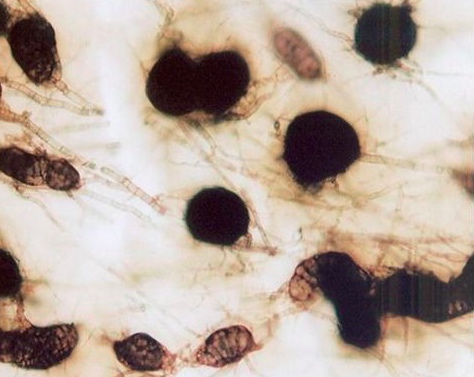
- Mycelium - septate, dark brown in colour with constriction at hyphal branches
- Sclerotia - minute, round, smooth, and black in colour
- Pycnidia - globose, ostiolated and dark brown in colour
- Pycnidiospores (Conidia) - thin walled, hyaline, single celled and elliptical
 Dry root rot infected plant
Dry root rot infected plant
Survival and mode of spread
- Survival: In infected debris as facultative saprophyte and in soil as facultative parasite
- Primary spread: Seed-borne and soil-borne sclerotia
- Secondary spread : Air borne pycnidiospores
Favourable conditions
- Day temperature: 30°C and above
- Prolonged dry season followed by irrigation
Integrated disease management
- Seed treatment with Trichoderma asperellum @ 4 g/kg or Bacillus subtilis @ 10 g/kg of seed
- Basal application of zinc sulphate @ 25 kg/ha
- Basal application of neem cake @ 150 kg/ha
- Soil application of T. asperellum – 2.5 kg / ha + 250 kg of well decomposed FYM at 30 days after sowing
- Spot drenching with Carbendazim 50 WP @ 1 gm/ lit
|
|


