| Crown rot: Rhizoctonia solani |
Symptom:
- Damping-off of carrot seedlings and a crown rot later and during storage
- Field symptoms include premature senescence and death of foliage
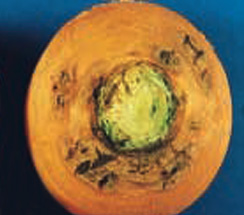
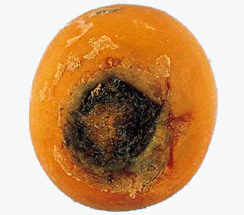
- On carrot roots - dark brown sunken lesions or cankers near the crown or in other parts of the root – cavity spot
|
| |
 |
 |
 |
| |
Initial symptom |
Dark Brown sunkern leisons |
Infected carrots |
|
Identification of pathogen:
- Sclerotia - irregular, brown to black and 5mm in diameter
- Fungus produces both terminal and intercalary, barrel shaped chlamydospore
Mode of spread and survival:
- R. solani overwinters in soils as mycelia on plant debris and as dark brown sclerotia that remain in soil for long periods
- R. solani can spread from plant to plant in closely spaced carrots when the canopy is fully formed
Epidemiology
- More severe on muck-grown carrots
- Warm temperatures and wet conditions - especially when these environmental conditions occur near harvest
|
Management:
- Cultural practices that reduce crown injury and enhance soil drainage and air circulation within the canopy are recommended
- Plant debris from previous crops should be removed before planting carrots
- Carrots should not follow perennial crops such as alfalfa
- Quintozene – sprayed in the soil before sowing-effective control
|
Source of Images:
http://www.carrotmuseum.co.uk/photos/carrot-disorders-diseases.pdf |



