Post Harvest Diseases:: Vegetables:: Carrot
| Crater rot: Rhizoctonia carotae |
Symptom:
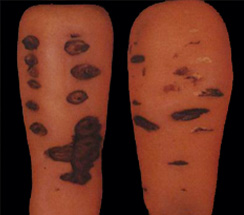
- Band of dark brown necrosis around the crown and horizontal brown canker-like lesions mostly on the crown and upper roots
- Small pits subsequently developed beneath the lesions, that enlarged into sunken brown crater lines with a white, flocculent mycelium produced under high humidity
Bitterness:
- Carrots can develop off-flavours or bitterness in cool storage. The cause of these off-flavours is the production of compounds in carrots called isocoumarins. Isocoumarins develop when carrots are exposed to ethylene.
- Ethylene is a gas produced naturally by many fruits and vegetables, such as apples, bananas and tomatoes during ripening.
- Carrots can be stored in sealed plastic bags in domestic refrigerators containing ethylene producing fruit.
Phenolic browning:
- Phenolic browning (or surface browning) is seen as a browning or discoloration of the surface of carrot.
- It can develop when carrots are washed and stored in cool rooms for long periods before packing.
- Abrasion caused by mechanical washing often removes the epidermal layer (outer skin), exposing the carrot tissue to oxidation of phenolic compounds, which turn brown, or black in severe cases.
- Phenolic browning can be confused with ‘5 o’clock shadow’ or boron deficiency of carrots. Phenolic browning can be confused with ‘5 o’clock shadow’ or boron deficiency of carrots.
- The latter is seen as many small brown spots under the skin, causing the root to look dull.
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Dark brown necrosis |
|
Canker-like lesions |
|
|
Identification of pathogen:
- Bacteria is gram –ve, motile with large peritrichous flagella
Mode of spread and survival:
- Soil - source of primary inoculum
- Survive in decaying refuse and enter the root principally through cultivation wounds, harvest bruises, freezing injury, and insect openings
- Flies- Hylemus cillicrura, H. brassicae carry the bacteria in their intestinal tracts
|
Management:
- Rapid removal of field heat.
- Application of Dowicide (Ophenylphenol) @ 98 g/L
- 6-methoxy mellen increase resistance
- Cholorothalonil – Seed and soil application
- 8 years rotation with non host crop
- Using disease free seed.
- Bacillus subtilis & T.viride application
|
Source of Images:
http://phytopath.ca/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/DPVCC-colour-plates-chapter-6-carrot.pdf
|
|


