Agricultural crops :: Cash crops :: Sugarcane
Rust: Puccinia erianthi |
Symptoms:
- The earliest symptoms are small, elongated yellowish spots that are visible on both leaf surfaces.
- The spots increase in length, turn brown to orange-brown or red-brown in color, which coalesced and formed large, irregular necrotic areas, thus it shows rusty appearance of leaf.
- This eventually resulted in premature death of the leaves.
|
|
Pathogen:
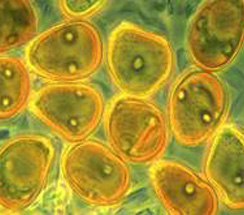
- Uredinia are elongate, reddish-brown, with capitate, hyaline to light brown paraphyses.
- Urediniospores are thick-walled, orange-brown, obovoid, measuring 26-34 x 16-20 µm. The urediniospore surface is echinulate with 4-5 equatorial pores.
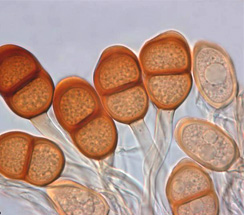
- Teliospores are dark brown and measure 30-43 x 17-23 µm, clavate, two-celled and slightly constricted at the septum.
Management strategies
Cultural method
- The best means of control for sugarcane rust is to grow resistant varieties Use resistant varieties like Co 91010 (Dhanush), Co 87025 (Kalyani)
- Affected leaves should be remove and burn immediately
- Sugarcane grown in fields receiving recent applications of mill mud is typically very prone to rust
|
| |
 |
|
 |
|
| |
Puccinia erianthi |
|
Teliospores |
|
|
Chemical method
- Spray Tridemorph 1.0 litres or Mancozeb 2.0 kg/ha.
- Use dithane M 45 @ 2 g/lit for one spraying.
- Application of triazole or strobilurin or pyraclostrobin fungicide @ 3 g/ lit of water.
|
|





