Agricultural crops :: Cash crops :: Sugarcane
Red rot: Glomerella tucumanensis |
Symptoms:
- The affected canes exhibit leaf colour change, from green to orange and then to yellow in the third or fourth leaf. Then the leaves start drying from bottom to top.
- If the fungal spores enter the leaf sheath through the leaf midrib, then reddish spots can be seen on the back side of the leaf midrib also.
- The external symptoms appear only after16 - 21 days after infection and drying of entire cane takes another 10 days time.
- When the affected cane is split opened, the inner region is reddish in colour with intermittent white tinges across the cane length.
- Sometimes, the pith inside the cane is filled with blackish brown liquid and exhibited alchohol odour.
|
|
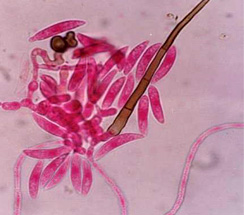
Pathogen:
- Red rot disease is caused by the fungus Glomerella tucumanensis. An older name, Colletotrichum falcatum, is still preferred by some pathologists.
- Pathogen present on leaf sheaths and blades, solitary or aggregated, often forming short lines between vascular bundles, globose, immersed, dark brown to black 65-250 µm dia.; wall up to 8 cells thick, sclerotia on outside, pseudoparenchymatous within, ostiole slightly papillate, circular.
Management strategies:
Cultural method:
- The best way to control red rot is to select setts for planting from healthy plants in a disease- free area.
- The red rot affected field must be rotated with rice for one season and other crops for two seasons.
- Growing of recommended resistant and moderately resistant varieties viz., Co 86032, Co 86249, CoSi 95071, CoG 93076, CoC 22, CoSi 6 and CoG 5
|
| |
 |
|
| |
Glomerella tucumanensis |
|
|
Physical method:
- Removal of the affected clumps at an early stage and soil drenching with Carbendazim 50 WP (1 gm in 1 litre of water)
- The cut ends and entire setts should be dipped in a fungicide solution, such as one per cent Bordeaux mixture.
- If the disease is noticed in the field, the leaves and canes should be collected and destroyed by burning.
Chemical method:
- Adopt sett treatment with Carbendazim before planting (Carbendazim 50 WP (0.5 gm in 1 litre of water) or Carbendazim 25 DS (1gm in 1 litre of water) along with 2.5 kg of Urea in 250 litre of water
- Use fungitoxic chemicals like Bavistan, Benomyl, Topsin and Aretan at 0.1 per cent for 18 min. at 52ºC for dipping setts which gave almost complete elimination of rot infection.
|
|




