Amla (Phyllanthus emblica)
Euphorbiaceae
Varieties
The most popular cultivable varieties of amla are Banarasi, NA 7, Krishna, Kanchan, Chakaiya, BSR 1.
Soil and climate
Amla is a subtropical plant and prefers dry climate. It is a hardy plant and can be grown in variable soil conditions. The crop can tolerate salinity and alkalinity.
Planting material
Seedlings, Grafts and Buddings are used for planting.
 
Amla grafts
Planting
Planting is done during July-August with a spacing of 6 x 6 m in pits of 1x1m or 1.25 x 1.25m.

High density planting
 
Black polythene mulch Dry grass mulching
Irrigation
Irrigate the plants initially for establishment. No irrigation is required during rainy and winter season. Drip irrigation is appropriate which can save water upto 40-45%.

Drip irrigation
Manures and fertilizers (per plant/year)
Manures and Fertilizers |
Bearing tree |
FYM |
10 kg |
N |
200 g |
P |
500 g |
K |
200 g |
Manuring should be done immediately after pruning.
Training and pruning
The main branches should be allowed to appear at a height of 0.75-1 m above the ground level. Plants should be trained to modified central leader system. Two to four branches with wide crotch angle, appearing in the opposite directions should be encouraged in early years.
During March – April, prune and thin the crowded branches to provide maximum fruit bearing area in the tree.
Stem swelling

|
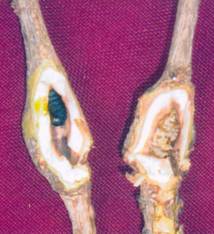
|
Stem bulging |
Control
- Stem swelling / bulging can be controlled by proper pruning
Plant protection
Pest
Gall caterpillar
Young caterpillars bore into the apical portion of the shoot during rainy season and make tunnel. Due to this, apical regrowth is checked, side shoots develop below the gall and subsequent growth in following season is greatly hampered. Cutting off the infected apices and prophylactic spray of systemic insecticide like Dimethoate 0.03 percent will control the pest.
Bark eating cater pillar
Damages the stem and branches of grown up trees by eating the bark. The affected portion should be cleared and few drops of kerosene should be applied in holes to keep this in control.
Disease
Rust
Rust appears as circular reddish solitary or gregarious on leaves and also on fruits. Spray 0.2 per cent Mancozeb at an interval of 7 to 28 days during July to September.
Yield
The crop yields about 100 kg/tree annually.
 
Grading and packing
Market information
| Growing Districts |
Tirunelveli, Dindigul, Sivagangai, Thoothukudi |
Major Markets in Tamil Nadu |
Koyambedu market, Chennai, Ottanchathiram |
Preferred Varieties and Hybrids |
BSR 1, NA-7 |
|











