This is a polyphagous pest infesting most cultivated crops. It is a major pest of tomato as well and is widely distributed throughout India.
Life cycle (4–6 weeks)
The adult moths are medium sized, stout and pale brown in colour with a reddish brown tinge. The forewings are olive green to pale brown in colour with a circular brown spot at the centre. The hind wings are smoky white in colour with a broad dull blackish outer border.
The eggs are ribbed, dome-shaped and yellowish white. The freshly hatched larvae are yellowish white and the fully grown caterpillars are in varied colours. They are mostly apple green with white and dark grey longitudinal lines. They have a white wavy line on the lower lateral part of the body. The eggs are laid on the leaves and flowers. At times, they are also found on young fruits. Pupation occurs in the soil.
Damage pattern
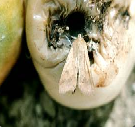
The young larvae feed on the tender leaves. At later stages, they attack the fruits and bore circular holes. Usually the larvae thrust only their heads inside the fruits. They move from one fruit to another, causing damage. Externally, the damage appears in the form of holes. They are found from flowering to harvest stage, especially during July to November.
Economic threshold level :
2 larvae / 2 m row length
Management
- Monitor top three leaves for Helicoverpa eggs and hand pick larvae.
- Intercropping tomato with marigold is an effective IPM practice. Planting of the trap crop should be adjusted in such a manner that tomato flowering coincides with the tight bud stage of the marigolds. Marigolds attract both fruit borer and leaf miner adults for egg laying.
- Growing sorghum (8 rows) as a border crop around the field at 30 x 10 cm spacing promotes natural predators like Chrysoperla and Coccinellids.
- Place 15–20 bird perches per hectare. This invites predatory birds.
- Spray 5% neem seed kernel extract, Andrographis kashayam or five leaf extract to kill larvae at their early stages.
- Soil application of the seed extracts of Strychnos nux-vomica @ 1.5 gm/plant at an interval of 20 days, twice, when there is severe borer attack.
Use of biocontrol agents like NPV (@ 250 LE/ha), Bacillus thuringiensis (@ 1 gm/litre of water), Trichogramma chilonis (@ 50,000 eggs/ha, six times at weekly intervals) and Bracon hibitor (larval parasite). |