CONTRACT FARMING IN FORESTRY
|
|
|
CONTACT ADDRESSES OF COMPANIES INVOLVED IN CONTRACT FARMING OF :
|
Contract farming is the contractual arrangement between farmer and the firm, whether oral or written, specifying one or more conditions of production and/or marketing of an agricultural product. Contract farming minimally demands a crop agreement made in advance, the firms, in varying degrees, shares the decision making power with the farmer. The farmer lends to the production process labour and land in his possession. Conversely the firm provides some of the production, knowledge inputs, marketing facility and participates in production decision and supervision (Watts, 1994).
OBJECTIVES OF CONTRACT FARMING |
|
-
Supplying planting material
-
Guiding production of crops
-
Facilitate bank loan
-
Assured buy back agreement
TYPES OF CONTRACT FARMING |
|
Several types of contracts are distinguished according to the sharing of risks and specification of contract terms. From the management view point, two types of contracts are determined.
- Limited Management Contract where a farmer gets production input and sells the produce to the firm. There is no real guarantee for the price for the produce.
- Full Management Contract where the farmer and the firm have entered into contract for certain amount of production. In this kind of contract the price is announced before the season thus the price risk is minimised. The firm provides market for the produce provided the quality specifications are met.
Khols and Uhl (1985) classified contracts into three broad categories.
- Market specification contract where contract is a pre-harvest arrangement that binds the firm and grower to a particular set of conditions governing the sale of the crop. These conditions often specify price, quality and timing of delivery of the produce.
- Resource providing contract where the contract oblige the contracting firms to supply production inputs, extension or credit in exchange for a marketing arrangement.
- Management and income guaranteeing contract where contract includes the production and marketing stipulations of the former two types. In addition, market and price risks were transferred from farmers to firm and the farmer is assured of a certain level of revenue. But the contracting firms take a substantial part of the managerial responsibility of the farmer. The various classifications of the contracts can be explained in the table below.
Types of Contract
| S.No. |
Types of contracts |
Provision of Inputs |
Provision of market for output |
Price guarantee |
Income guarantee |
| 1 |
Limited Management Contract |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
| 2 |
Full Management Contract |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
| 3 |
Market Specification Contract |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
| 4 |
Resource Providing Contract |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
No |
| 5 |
Income Guaranteeing Contract |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Contract Farming Model
To meet the above needs and increase the area under pulp wood plantation through farm forestry, the two paper industries in association with Tamil Nadu Agricultural University has developed a tripartite and quad-partite model for promotion of pulp wood based contract farming system. Through the system, it is intended to produce quality and sustained raw material through a strong supply chain.
Tri-partite Model
This model incorporates industry, growers and financial institutions. Under this system, the industry supplies quality planting material at subsidized rate and assures minimum support price of Rs. 2000 per tonnes or the prevailing market price whichever is higher. The financial institutions viz., Indian Bank, State Bank of India and Syndicate Bank provide credit facilities to the growers at the rate of Rs. 15000 to 20000 per acre in three installments. For credit facilities, a simple interest rate at 8. 5 per cent is followed and the repayment starts after felling. The contract farming system extends no collateral security for loan amount up to Rs.1, 00,000/- per farmer.
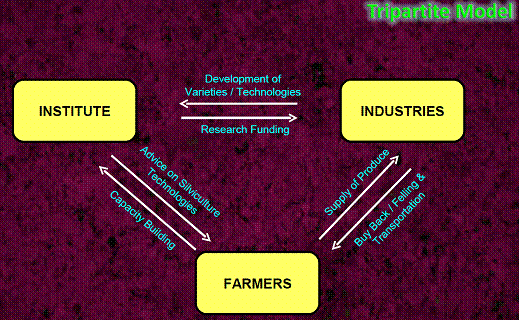 |
Fig 1. Tri-partite Model contract tree farming |
Quad-partite Model
This system is similar to tri-partite model barring the involvement of research institute (Fig. 1). In this system, research institute particularly Forest College and Research Institute (TNAU) play a significant role for technological advancements through varietal development and also to advice site specific precision silvicultural technology to the growers. A pre and post-plantation scientific advice helps to develop human resources through on and off institute mode to farmers and plantation staff of the industries.
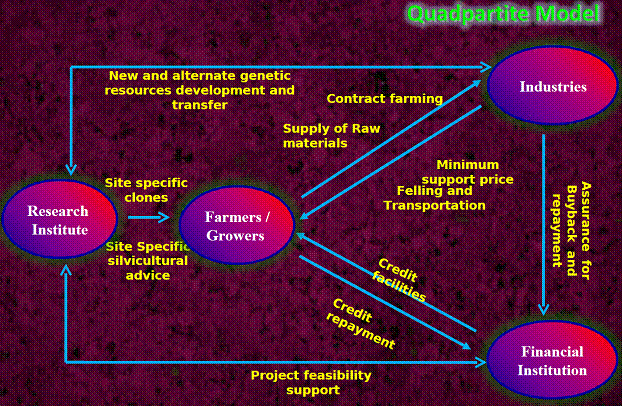 |
Fig 2. Quad-Partite Model contract tree farming |
Similarly, the industries mass multiply the potential genetic materials identified by the research institute in a decentralized manner and supply them at subsidized costs. The industry also facilitates felling and transport at their own costs, which resulted in strong linkage between industry and the farmers. The industry also help to repay the loan amount after felling of farm grown raw materials there by help the financial institutions for timely repayment, which resulted in strong institutional mechanism for sustainability of the contract tree farming system in the state.
Source: http://www.fcrinaip.org/contractfarming.php
|


